Python Tools
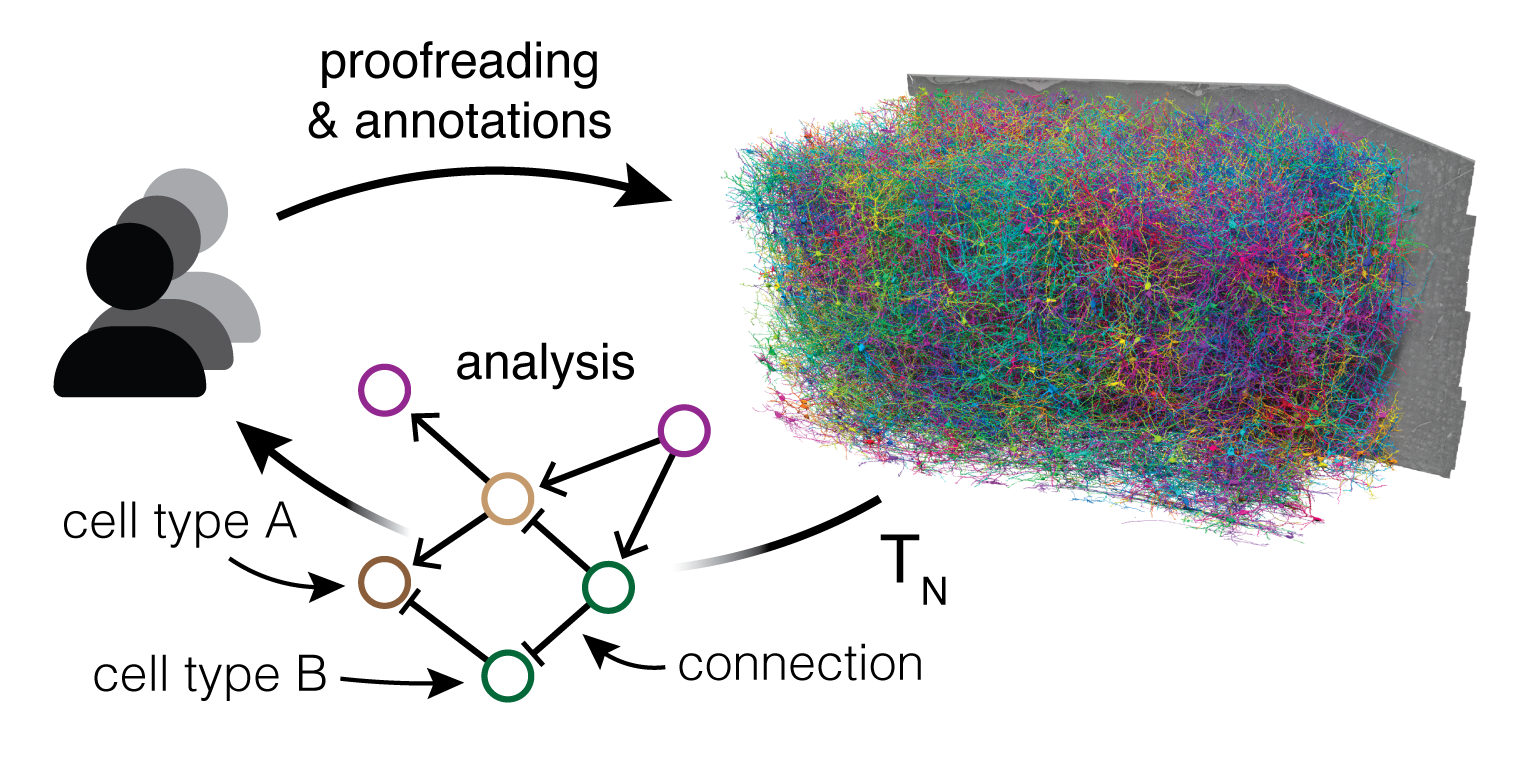
The MICrONS dataset, spanning one cubic millimeter of mouse cortex, is comprised of petabytes of data from 1) in vivo functional imaging, 2) electron microscopy images at nanometer resolution, 3) dense segmentation of 200,000 brain cells, and 4) half a billion synapses, and 5) hundreds of thousands of other annotations to label the data.
To enable systematic analysis without downloading hundreds of gigabytes of data, users can selectively access cloud-based data programmatically through a collection of open source Python clients:
| Tool Name | Data Products | URLs |
|---|---|---|
| cloud-volume | EM imagery, voxel segmentation, and meshes | https://github.com/seung-lab/cloud-volume |
| MeshParty | EM meshes and skeletons | https://github.com/CAVEconnectome/MeshParty |
| CAVEclient | EM structural annotations (synapses, cell-types, etc.) segmentation edits, local geometric properties | https://github.com/CAVEconnectome/CAVEclient |
| microns-nda | Functional imaging DataJoint database | https://github.com/cajal/microns-nda-access |
The functional data, including calcium traces, stimuli, behavioural measures and more, are available in a DataJoint database that can be accessed using DataJoint’s Python API, or is available as neurodata without borders (NWB) files on the Distributed Archives for Neurophysiology Data Integration (DANDI) Archive.
EM imagery and segmentation volumes are hosted on Google or AWS servers, and accessed with the python client cloud-volume. Mesh files describing the shape of cells can be downloaded with cloud-volume, which also provides features for convenient mesh analysis, skeletonization and visualization.
These meshes can be decomposed and richly annotated for automated proofreading and morphological analysis of processes and spines using NEURD. For more, see reference: (Celii et al. 2025)
Annotations on the structural data, such as synapses and cell body locations, can be queried via CAVE client, a Python interface to the Connectome Annotation Versioning Engine (CAVE) APIs. CAVE encompasses a set of microservices for collaborative proofreading and analysis of large-scale volumetric data. For more, see reference: (Dorkenwald et al. 2025)
The Quickstart Notebooks in this section provide an introduction to CAVE, and examples of how to interact with CAVEclient, MeshParty, and cloud-volume.
![]()

